What is the correction factor for inductive sensors?
Correction factor for inductive sensors
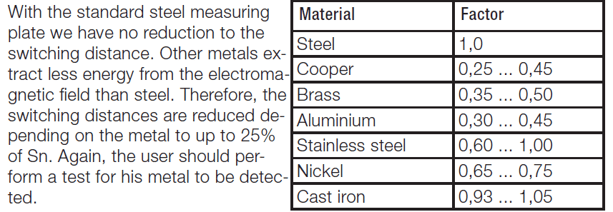
Some applications have multiple materials that have to be detected. When specifying a standard inductive proximity sensor the first question asked is, “what is the target material that will need to be detected.” The ideal target for an inductive sensor is a target made from mild steel. This is correct; however, an inductive sensor can also detect non-ferrous materials but a correction factor has to be determined into the rated operating distance of your selected sensor. For example, if you select a sensor that has 4 mm of operating distance (Rated Operating Distance), and the target is aluminum, we would multiply a correction factor of 0.30-0.45 to get the new rated operating distance of your sensor (1.2 mm -1.8 mm). Due to the aluminum’s non-ferrous material we can no longer achieve the 4 mm rated operating distance in proximity to the aluminum target.
The approximate detection distance of a sensor for various metals can be estimated using the correction factors below.
Learn more about inductive sensors